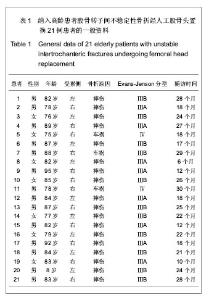
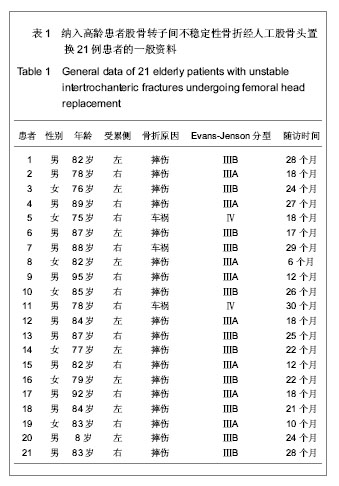
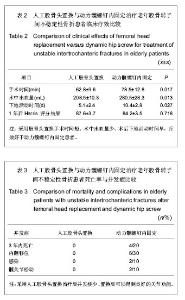
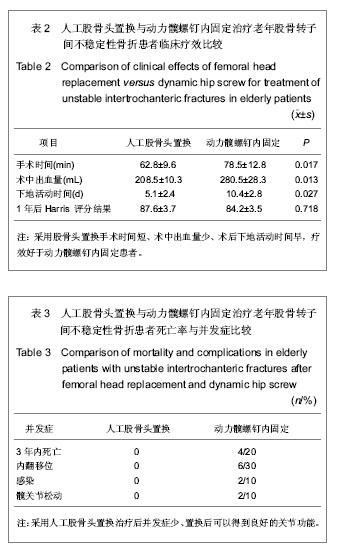
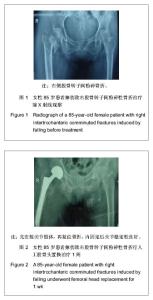
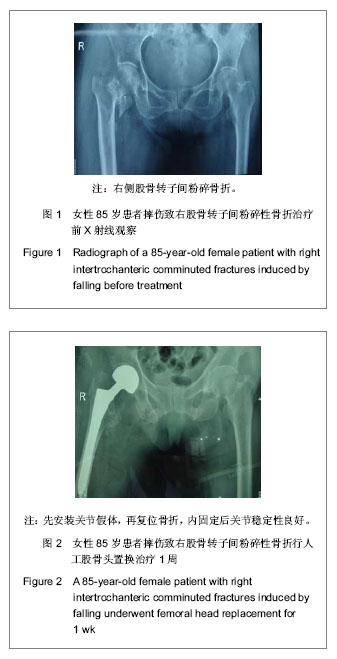
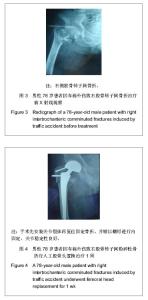
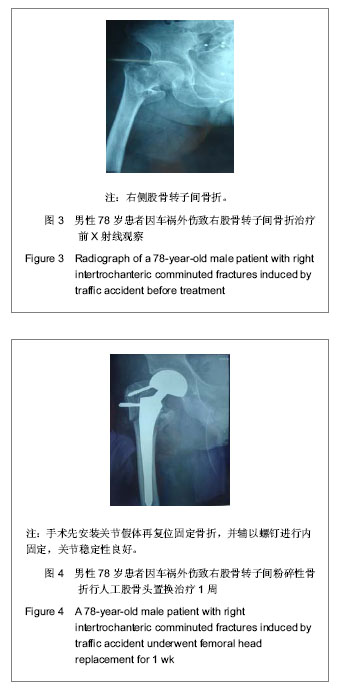
| [1] 李世民,党耕町.临床骨科学[M]天津:天津科学技术出版社,1998: 328.
[2] Luo J, Guo SC, Huang ZY, et al. Treatment of femoral unstable intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly with uncemented long stem bipolar prosthetie prosthesis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010;30(7):1685-1687
[3] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎,等.实用骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2008:710-711
[4] 中华医学会骨科学分会中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[CD/J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2009,3(3):70-72.
[5] 刘云鹏,刘沂骨与关节损伤和疾病的诊断分类及功能评定标准[M]北京:清华大学出版社,2002:216-217
[6] Gaumetou E, Zilber S, Hernigou P. Non-simultaneous bilateral hip fracture: epidemiologic study of 241 hip fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97(1):22-27.
[7] Grimsrud C, Monzon RJ, Richman J, et al. Cemented hip arthroplasty with a novel cerclage cable technique for unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20(3):337-343.
[8] 张怀华,孙永青.股骨粗隆间骨折术后患者死亡率分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(1):21-23
[9] 杨文斌,廖海浪,何福鲜,等.老年股骨粗隆闾骨折早期死亡原因分析[J]中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(4):348-349.
[10] [Han SK, Lee BY, Kim YS, et al. Usefulness of multi-detector CT in Boyd-Griffin type 2 intertrochanteric fractures with clinical correlation. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(6):543-549.
[11] Han SK, Lee BY, Kim YS, et al. Usefulness of multi-detector CT in Boyd-Griffin type 2 intertrochanteric fractures with clinical correlation. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(6):543-549.
[12] Sancheti Kh, Sancheti P, Shyam A, et al. Primary hemiarthroplasty for unstable osteoporotic intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly: A retrospective case series. Indian J Orthop. 2010;44(4):428-434.
[13] 荣国威.译骨科内固定[M]北京:人民卫生出版社,1995:367.
[14] Setiobudi T, Ng YH, Lim CT, et al. Clinical outcome following treatment of stable and unstable intertrochanteric fractures with dynamic hip screw. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2011; 40(11):482-487.
[15] Li J,Chen JK,Zhou K,et al. Application of dynamic hip screw with modified reamer in intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly Zhongguo Gu Shang.2011;24(5):362-365.
[16] Gundle R, Gargan MF, Simpson AH. How to minimize failures of fixation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. 1995; 26(9):611-614.
[17] 王振东,樊强,李永德.人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄不稳定粗隆间骨折的疗效观察[J].中华损伤与修复杂志,2011,6(1):74-78.
[18] Sehmisch S, Rieckenberg J, Dresing K. Stabilization of unstable intertrochanteric fractures with the proximal femoral nail. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2013;25(1):63-83.
[19] 范少地,于杰,陈戎波,等.高龄股骨转子间骨折人工关节置换的特点及假体的选择[J]中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(48): 9061-9064.
[20] 何大川,程少华,潘华,等.重建粗隆及股骨矩关节置换治疗高龄不稳定粗隆间骨折[J]实用骨科杂志,2011,17(3):209-211.
[21] 李宝林,杨冰,韩红卫,等.半髋置换治疗高龄骨质疏松不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折[J]实用骨科杂志,2010,16(2):138-139.
[22] 林加阳,徐耿填,林勇彬,等.PFNA和股骨头置换治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效研究[J].中外医学研究,2012,10(9):5-6.
[23] 吴景冬.PFNA 内固定微创治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折体会[J].中外医学研究,2011,9(5):36-37.
[24] 敖沸,彭小龙,贾芝和,等.人工股骨头置换术治疗老年粉碎性股骨粗隆间骨折45例[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(21):4810-4811.
[25] Rowe SM, Yoon TR, Ryang DH. An epidemiological study of hip fracture in Honam, Korea. Int Orthop. 1993;17(3):139-143.
[26] Olsson LE, Karlsson J, Ekman I. The integrated care pathway reduced the number of hospital days by half: a prospective comparative study of patients with acute hip fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2006;1:3.
[27] 谭平先,任邵东,叶湖,等.高龄股骨粗隆问骨折髓关节置换手术策略的探讨[J]实用骨科杂志,2010,16(6):412-414.
[28] Jotanovic Z, Jurdana H, Sestan B. Hemiarthroplasty is an effective surgical method to manage unstable trochanteric fractures in elderly people. Coll Antropol. 2011,35(2):427-431.
[29] 王振东,樊强,李永德.人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄不稳定粗隆间骨折的疗效观察[CD].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2011, 6(1): 74-78.
[30] 邢建瑞,李艳,杨秀丽,等.人工股骨头置换治疗高龄不稳定股骨转子间骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2012,14(4):350-353. |